What is Partnership??
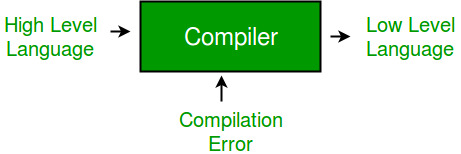
Partnership is the relation between two or more persons,who have agreed to share the profits of the business,which is carried on by all or any one of them acting for all. Partnership is governed by the “Indian Partnership Act 1932”.
Definition of Partnership?
According to the “Indian Partnership Act 1932”,”Partnership is the relationship between two persons,who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.”The persons who have entered a partnership with one another are individually called”Partners” and the association of these partner is called”firm.”
Maximum Limit of Partners
The new Companies Act 2013 has prescribed the maximum number of members in case of a partnership firm should not be more than 100 in case of partnerships. As per the previous Companies Act 1956, the maximum limit in case of partnerships was 10 and 20 for banking business and other businesses respectively.
Partnership Deed
When two or more persons join hands to set up a business and share its profits and losses it is called Partnership. Section 4 of the Indian Partnership Act 1932 defines partnership as the ‘relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all’.
Partnership deed generally contains the following details:
(1)Names and Addresses of the firm and its main business;
(2)Names and Addresses of all partners;
(3)A contribution of the amount of capital by each partner;
(4)The accounting period of the firm;
(5)The date of commencement of partnership;
(6)Rules regarding an operation of Bank Accounts;
(7)Profit and loss sharing ratio;
(8)The rate of interest on capital, loan, drawings, etc;
(9)Mode of auditor’s appointment, if any;
(10)Salaries, commission, etc, if payable to any partner;
(11)The rights, duties, and liabilities of each partner;
(12)Treatment of loss arising out of insolvency of one or more partners;
(13)Settlement of accounts on the dissolution of the firm;
(14)Method of a settlement of disputes among the partners;
(15)Rules to be followed in case of admission, retirement, a death of a partner; and
(16)Any other matter relating to the conduct of business. Normally, all the matters affecting the relationship of partners amongst themselves are covered in partnership deed.
What are the different types of partnership??
(1)Partnership at will
If there is no clause to establish a partnership at the expiry of such a partnership, it is referred to as a partnership at will. In accordance with Section 7 of The Indian Partnership Act, 1932, two conditions have to be met for a partnership to be a partnership at will and they are:
*There is no agreement on a fixed period for the existence of a partnership.
*No provision is made for establishing a partnership.
If a partnership has been established and continues to operate beyond the fixed period, the partnership will become a partnership at will after the end of that term.
(2)Particular Partnership
A partnership can be formed for ongoing business or for a particular purpose. If the partnership is only formed to carry out one company or complete one undertaking, it is known as a particular partnership.The partnership will be dissolved after the completion of the said venture or activity. The partners may, however, come to an agreement to continue the said partnership. But in the absence of this, when the task is complete, the partnership ends.
(3)Partnership for a Fixed Term
Now, during the establishment of a partnership, the partners may agree on the duration of this arrangement. This would mean that the partnership was established for a fixed period of time.Therefore, such a partnership will not be called a partnership at will, it will be a partnership for a fixed term. The partnership ends after the expiration of such a duration.However, there may be cases where the partners continue their business even after the expiry of the duration. They continue to share profits and there is a component of a mutual agency. Then in such a case, the partnership will be at will.
(4)General Partnership
When the purpose of forming the partnership is to carry out the business in general, it is said to be a general partnership.Unlike a particular partnership, in a general partnership, the scope of the business to be carried out is not defined, so all the partners are accountable for all the actions of the partnership.
Partnership is the relation between two or more persons,who have agreed to share the profits of the business,which is carried on by all or any one of them acting for all. Partnership is governed by the “Indian Partnership Act 1932”.
Definition of Partnership?
According to the “Indian Partnership Act 1932”,”Partnership is the relationship between two persons,who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.”The persons who have entered a partnership with one another are individually called”Partners” and the association of these partner is called”firm.”
Maximum Limit of Partners
The new Companies Act 2013 has prescribed the maximum number of members in case of a partnership firm should not be more than 100 in case of partnerships. As per the previous Companies Act 1956, the maximum limit in case of partnerships was 10 and 20 for banking business and other businesses respectively.
Partnership Deed
When two or more persons join hands to set up a business and share its profits and losses it is called Partnership. Section 4 of the Indian Partnership Act 1932 defines partnership as the ‘relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all’.
Partnership deed generally contains the following details:
(1)Names and Addresses of the firm and its main business;
(2)Names and Addresses of all partners;
(3)A contribution of the amount of capital by each partner;
(4)The accounting period of the firm;
(5)The date of commencement of partnership;
(6)Rules regarding an operation of Bank Accounts;
(7)Profit and loss sharing ratio;
(8)The rate of interest on capital, loan, drawings, etc;
(9)Mode of auditor’s appointment, if any;
(10)Salaries, commission, etc, if payable to any partner;
(11)The rights, duties, and liabilities of each partner;
(12)Treatment of loss arising out of insolvency of one or more partners;
(13)Settlement of accounts on the dissolution of the firm;
(14)Method of a settlement of disputes among the partners;
(15)Rules to be followed in case of admission, retirement, a death of a partner; and
(16)Any other matter relating to the conduct of business. Normally, all the matters affecting the relationship of partners amongst themselves are covered in partnership deed.
What are the different types of partnership??
(1)Partnership at will
If there is no clause to establish a partnership at the expiry of such a partnership, it is referred to as a partnership at will. In accordance with Section 7 of The Indian Partnership Act, 1932, two conditions have to be met for a partnership to be a partnership at will and they are:
*There is no agreement on a fixed period for the existence of a partnership.
*No provision is made for establishing a partnership.
If a partnership has been established and continues to operate beyond the fixed period, the partnership will become a partnership at will after the end of that term.
(2)Particular Partnership
A partnership can be formed for ongoing business or for a particular purpose. If the partnership is only formed to carry out one company or complete one undertaking, it is known as a particular partnership.The partnership will be dissolved after the completion of the said venture or activity. The partners may, however, come to an agreement to continue the said partnership. But in the absence of this, when the task is complete, the partnership ends.
(3)Partnership for a Fixed Term
Now, during the establishment of a partnership, the partners may agree on the duration of this arrangement. This would mean that the partnership was established for a fixed period of time.Therefore, such a partnership will not be called a partnership at will, it will be a partnership for a fixed term. The partnership ends after the expiration of such a duration.However, there may be cases where the partners continue their business even after the expiry of the duration. They continue to share profits and there is a component of a mutual agency. Then in such a case, the partnership will be at will.
(4)General Partnership
When the purpose of forming the partnership is to carry out the business in general, it is said to be a general partnership.Unlike a particular partnership, in a general partnership, the scope of the business to be carried out is not defined, so all the partners are accountable for all the actions of the partnership.